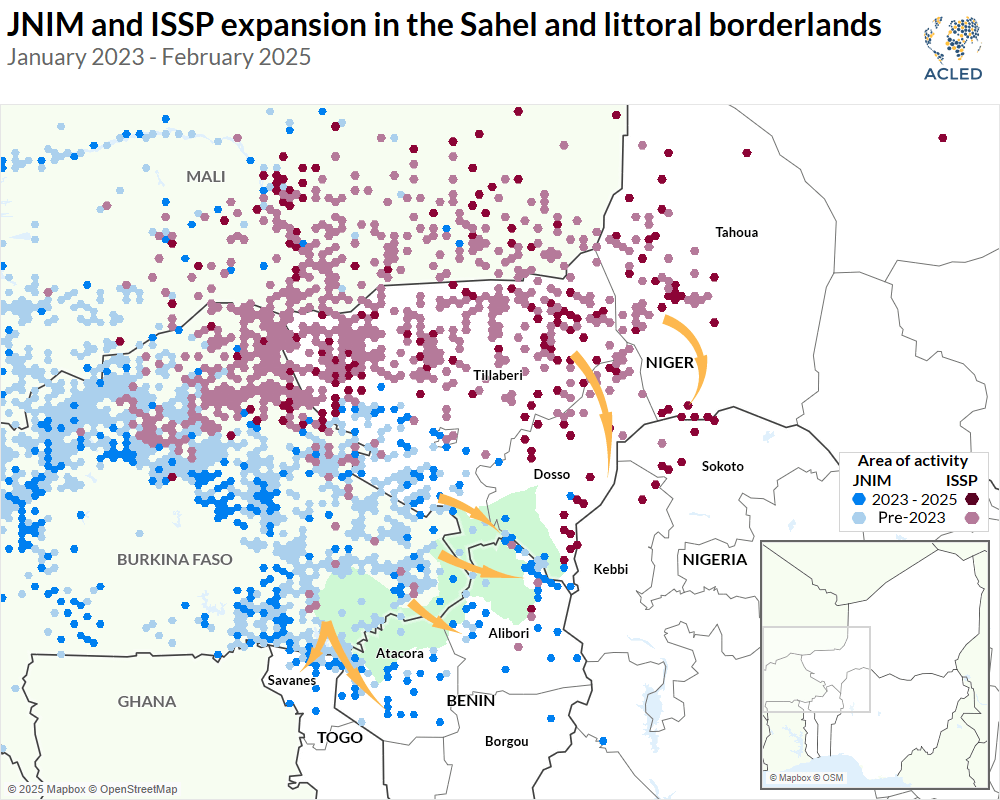
Benin, Niger, Nigeria: A New Jihadist Frontline?
Editor's Note: The escalating jihadist threat across Benin, Niger, and Nigeria has reached a critical juncture. This article examines the evolving dynamics and potential consequences of this increasingly volatile region.
1. Why This Topic Matters
The interconnectedness of Benin, Niger, and Nigeria is creating a dangerous new frontline in the fight against jihadism. While Boko Haram has long plagued the Lake Chad Basin, impacting Nigeria and Niger, the conflict is expanding geographically and strategically. This expansion threatens regional stability, displaces millions, fuels humanitarian crises, and poses a significant threat to international security. Understanding the evolving nature of this conflict, the actors involved, and the potential consequences is crucial for policymakers, aid organizations, and concerned citizens alike. This article will explore the key drivers of this escalating crisis, examine the tactics employed by jihadist groups, and analyze the implications for the wider Sahel region.
2. Key Takeaways
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Geographic Expansion | Jihadist groups are expanding their reach beyond traditional strongholds. |
| Increased Brutality | Tactics are becoming increasingly violent and indiscriminate. |
| Weak Governance | Fragile state institutions struggle to provide security and counter insurgency. |
| Transnational Networks | Jihadist groups operate across borders, hindering effective countermeasures. |
| Humanitarian Crisis | Displacement and violence fuel a growing humanitarian emergency. |
3. Main Content
3.1 Benin, Niger, Nigeria: A Shifting Battlefield
The Sahel region is experiencing a surge in jihadist activity, with Benin, Niger, and Nigeria forming a crucial and increasingly volatile nexus. While Boko Haram’s presence in northeast Nigeria has been well-documented, the spillover effect into neighboring Niger and the expansion into Benin represent a significant escalation. Groups like the Islamic State in the Greater Sahara (ISGS) and affiliated factions are actively exploiting porous borders and weak governance to establish a foothold and expand their influence. This interconnectedness allows for easy movement of fighters, weapons, and resources, making a coordinated regional response critical.
Key Aspects:
- Porous Borders: The lack of effective border control allows for the easy movement of militants and resources.
- Weak Governance: Corrupt or ineffective governance creates power vacuums that jihadist groups exploit.
- Climate Change: Drought and resource scarcity exacerbate existing tensions and create recruitment opportunities.
- Ethnic and Religious Divisions: Existing societal fault lines are exploited to further destabilize the region.
Detailed Analysis: The ISGS, for example, utilizes hit-and-run tactics, targeting security forces and civilians alike. Their brutality, including mass killings and kidnappings, serves to instill fear and undermine government authority. This tactic creates a cycle of violence, further destabilizing the region and leading to mass displacement. The weak state response coupled with the growing jihadist influence is breeding a sense of insecurity among communities, making them increasingly vulnerable to recruitment.
3.2 Interactive Elements on the Jihadist Threat
The conflict is not static; it is a dynamic and evolving situation characterized by complex interactions between various actors.
Facets:
- Recruitment: Jihadist groups actively recruit disillusioned youth, often promising economic opportunities or religious salvation.
- Financing: Criminal activities, such as smuggling and kidnapping, provide crucial funding for these groups.
- International Involvement: Regional and international actors play a critical role, though the effectiveness of their interventions varies.
- Community Resilience: Some communities demonstrate remarkable resilience, actively resisting jihadist influence.
Summary: Understanding these interactive elements is crucial to designing effective counter-terrorism strategies. A solely military approach is unlikely to succeed; a holistic strategy encompassing governance reforms, economic development, and community engagement is paramount.
3.3 Advanced Insights on the Crisis
The scale of the humanitarian crisis associated with the escalating jihadist threat is profound. Millions have been displaced, facing food insecurity, lack of access to healthcare, and the trauma of violence.
Further Analysis: The displacement of populations creates further instability, straining resources in already fragile areas and exacerbating existing societal tensions. Furthermore, the destruction of infrastructure and disruption of economic activity hinder recovery efforts and perpetuate a cycle of poverty and instability.
Closing: The conflict in the Benin, Niger, Nigeria region demands a multifaceted, regionally coordinated, and internationally supported response. Ignoring this growing crisis will have severe and far-reaching consequences for the entire Sahel region and beyond.
4. People Also Ask (NLP-Friendly Answers)
Q1: What is the main driver of the conflict in this region? A: The main driver is the expansion of jihadist groups exploiting weak governance, porous borders, and societal divisions.
Q2: Why is this conflict important to the international community? A: This conflict threatens regional stability, fuels humanitarian crises, and poses a significant threat to international security due to its transnational nature.
Q3: How can I help? A: You can support humanitarian aid organizations working in the region, advocate for stronger international cooperation, and raise awareness about this crisis.
Q4: What are the biggest challenges to resolving this conflict? A: The biggest challenges include weak governance, porous borders, the transnational nature of the groups, and the complex interplay of various actors.
Q5: What is the role of climate change? A: Climate change is exacerbating existing tensions, contributing to resource scarcity and creating fertile ground for recruitment by jihadist groups.
5. Practical Tips for Understanding the Benin, Niger, Nigeria Crisis
Introduction: Staying informed about this complex crisis requires utilizing reliable sources and understanding the key dynamics at play.
Tips:
- Follow reputable news organizations covering the Sahel region.
- Read reports from international organizations like the UN and the EU.
- Engage with academic research on the topic.
- Support organizations providing humanitarian aid.
- Advocate for policies that address the root causes of the conflict.
Summary: By staying informed and engaged, we can better understand this critical situation and contribute to finding sustainable solutions.
Transition: The conflict in the Benin, Niger, Nigeria region is a complex challenge demanding urgent attention.
6. Summary
The escalating jihadist threat across Benin, Niger, and Nigeria represents a serious security and humanitarian crisis. Understanding the interconnected nature of the conflict, the actors involved, and the underlying drivers is critical for developing effective counter-terrorism strategies and addressing the resulting humanitarian emergency. Regional and international cooperation is essential to effectively combat this growing threat and prevent further destabilization of the Sahel region.
7. Call to Action
Ready to dive deeper? Subscribe for more insights on the escalating jihadist threat in West Africa.